简介
pprof 是性能调试工具,可以生成类似火焰图、堆栈图,内存分析图等。
整个分析的过程分为两步:1. 导出数据,2. 分析数据。
使用
一、查看实时数据
import 包
import (
"net/http"
_ "net/http/pprof"
)在代码开始的地方添加,一般是在 main 的执行函数开始的地方
go func() {log.Println(http.ListenAndServe(":6060", nil))
}()然后打开浏览器输入:http://127.0.0.1:6060/debug/pprof/,即可查看实时的信息
- allocs:查看过去所有内存分配的样本。
- block:查看导致阻塞同步的堆栈跟踪。
- cmdline:当前程序的命令行的完整调用路径。
- goroutine:查看当前所有运行的 goroutines 堆栈跟踪。
- heap:查看活动对象的内存分配情况。
- mutex:查看导致互斥锁的竞争持有者的堆栈跟踪。
- profile:默认进行 30s 的 CPU Profiling,得到一个分析用的 profile 文件。
- threadcreate:查看创建新 OS 线程的堆栈跟踪。
- trace:略,trace 可以单独写一篇文章来介绍。
注意,默认情况下是不追踪 block 和 mutex 的信息的,如果想要看这两个信息,需要在代码中加上两行:
runtime.SetBlockProfileRate(1) // 开启对阻塞操作的跟踪,block
runtime.SetMutexProfileFraction(1) // 开启对锁调用的跟踪,mutex二、导出数据
有两种方式下载
直接运行go tool pprof http://localhost:6060/debug/pprof/XXX,其会自动下载数据到本地,然后供你分析。(这个命令具体怎么用,见后文)
方法二:
访问http://localhost:6060/debug/pprof/XXX,游览器就会提醒你下载文件。
这里有一个小点要注意,在这个页面下,点击 profile 和trace总是会下载文件。而点击其他链接会跳转到另一个页面,来展示一些数据,但是可读性也比较差。
如果点击profile,程序会开始进行半分钟(默认值)的 CPU 采样,然后才会下载文件。
在跳转到页面中,会发现 URL 带有 ?debug=1 的后缀,如果把这个后缀去掉,则也会提示你下载文件。
总之,目前这个页面最有用的数据就是直接看看协程数,看看同步数,看看堆和线程创建数。点进去的链接基本都没太强的可读性。操作到这里,能看到这个网页即可。
注:这里采用的是 将数据导出成文件:
分析数据
地址:https://chanjarster.github.io/post/go/pprof-explained/
文件导出的后在 go 环境下运行命令:
1. go tool pprof pprof.gos-game.alloc_objects.alloc_space.inuse_objects.inuse_space.004.pb
2. go tool pprof http://url 地址或者通过页面来分析
go tool pprof -http=:8000 pprof/pprof.gos-game.alloc_objects.alloc_space.inuse_objects.inuse_space.004.pb解读数据
解读 CPU
以文中提供的 CPU Profile 来举例说明,我们使用 go tool pprof -http=0.0.0.0:4231 havlak1 havalk1.prof 来观察
解读 Top
(pprof) top10
Total: 2525 samples
Flat Flat% Sum% Cum Cum% Name
298 11.8% 11.8% 345 13.7% runtime.mapaccess1_fast64
268 10.6% 22.4% 2124 84.1% main.FindLoops
251 9.9% 32.4% 451 17.9% scanblock
178 7.0% 39.4% 351 13.9% hash_insert
131 5.2% 44.6% 158 6.3% sweepspan
119 4.7% 49.3% 350 13.9% main.DFS
96 3.8% 53.1% 98 3.9% flushptrbuf
95 3.8% 56.9% 95 3.8% runtime.aeshash64
95 3.8% 60.6% 101 4.0% runtime.settype_flush
88 3.5% 64.1% 988 39.1% runtime.mallocgc先了解是如何采样的:
- 采样频率是每秒 100 次
- 一个样本包含 goroutine 栈的程序计数器(program counters)
- 每次只会采样调用栈的前 100 行
原文中没有给出列名,这里给了出来,下面是解释:
- Total:总共采样次数,这里是 2525 次。
- Flat:函数在样本中处于运行状态的次数。简单来说就是函数出现在栈顶的次数,而函数在栈顶则意味着它在使用 CPU。
- Flat%:Flat / Total。
- Sum%:自己以及所有前面的 Flat% 的累积值。解读方式:表中第 3 行 Sum% 32.4%,意思是前 3 个函数(运行状态)的计数占了总样本数的 32.4%
- Cum:函数在样本中出现的次数。只要这个函数出现在栈中那么就算进去,这个和 Flat 不同(必须是栈顶才能算进去)。也可以解读为这个函数的调用次数。
- Cum%:Cum / Total
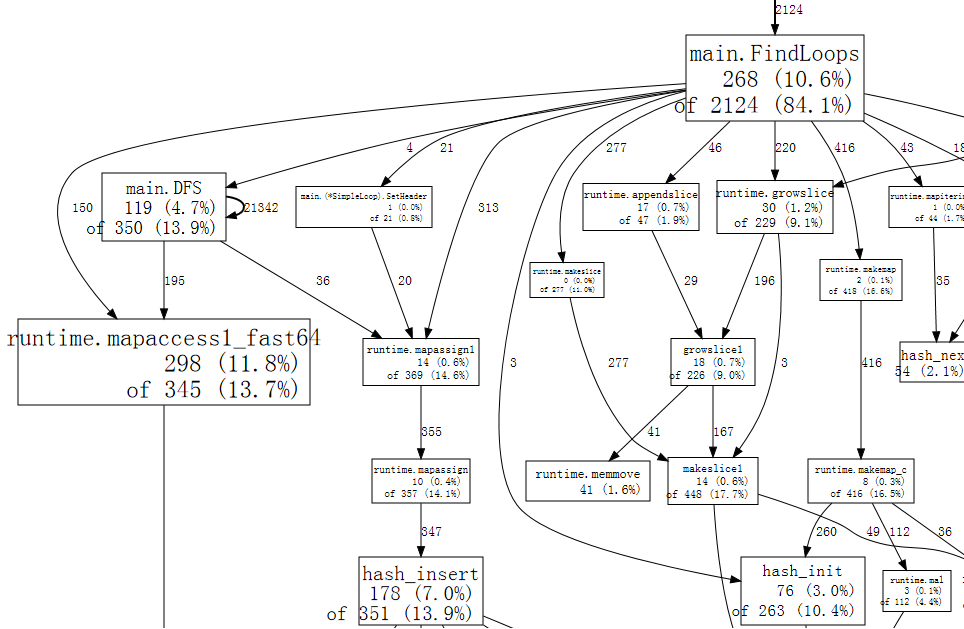
- 方框:函数
- 方框尺寸:代表了 Flat 的次数
- 箭头:X 调用 Y
- 线条:记录了 X 调用 Y 的次数。数字越大,线条越粗。图中 main.DFS 有一个指向自己的箭头,说明存在递归调用,而且调用了 21342 次()。
- 方框第一行数字:Flat (Flat%),栈顶次数
- 方框第二行数字:Cum (Cum%),调用次数
解读源码
(pprof) list DFS
Total: 2525 samples
ROUTINE ====================== main.DFS in /home/rsc/g/benchgraffiti/havlak/havlak1.go
119 697 Total samples (flat / cumulative)
3 3 240: func DFS(currentNode *BasicBlock, nodes []*UnionFindNode, number map[*BasicBlock]int, last []int, current int) int {1 1 241: nodes[current].Init(currentNode, current)
1 37 242: number[currentNode] = current
. . 243:
1 1 244: lastid := current
89 89 245: for _, target := range currentNode.OutEdges {9 152 246: if number[target] == unvisited {7 354 247: lastid = DFS(target, nodes, number, last, lastid+1)
. . 248: }
. . 249: }
7 59 250: last[number[currentNode]] = lastid
1 1 251: return lastid
(pprof)- 第一列:Flat
- 第二列:Cum
- 第三列:行号
下面是在 Web 界面看到的报告(基本差不多,见这里):
havlak1
Total: 5758 samples
main.DFS
/home/rsc/g/benchgraffiti/havlak/havlak1.go
Total: 225 2296 (flat / cumulative samples)
235 return false
236 }
237
238 // DFS - Depth-First-Search and node numbering.
239 //
240 3 3 func DFS(currentNode *BasicBlock, nodes []*UnionFindNode, number map[*BasicBlock]int, last []int, current int) int {241 18 19 nodes[current].Init(currentNode, current)
242 166 number[currentNode] = current
243
244 2 2 lastid := current
245 167 167 for _, target := range currentNode.OutEdges {246 17 508 if number[target] == unvisited {247 10 1157 lastid = DFS(target, nodes, number, last, lastid+1)
248 }
249 }
250 7 273 last[number[currentNode]] = lastid
251 1 1 return lastid
252 }
253
254 // FindLoops
255 //
256 // Find loops and build loop forest using Havlak's algorithm, which解读内存
以文中提供的内存 Profile 来举例说明,我们使用 go tool pprof -http=0.0.0.0:4231 havlak3 havalk3.mprof 来观察。
pprof 提供了 4 种视角,默认是-inuse_space:
-inuse_space:live object 占用内存-inuse_objects:live object 的数量-alloc_space:程序启动到现在,总共分配的内存-alloc_objects:程序启动到现在总共 object 的数量
(pprof) top5
Showing nodes accounting for 855.54MB, 46.66% of 1833.72MB total
Dropped 950 nodes (cum <= 9.17MB)
Showing top 5 nodes out of 164
flat flat% sum% cum cum%
463.33MB 25.27% 25.27% 463.33MB 25.27% su/goslib/core/persist.(*MsgCache).Add
117.76MB 6.42% 31.69% 403.70MB 22.02% su/game/confs/gen/pt.(*PlayerData).Unmarshal
96.16MB 5.24% 36.93% 96.16MB 5.24% su/game/app/models/data/user_data.SetExploreSite
91.09MB 4.97% 41.90% 93.59MB 5.10% su/game/app/task_observer.UpdateSub
87.20MB 4.76% 46.66% 87.20MB 4.76% su/game/confs/gen/pt.(*FreeBuildInfo).Unmarshal采样频率:
- 每分配 512K,采样一个 block(具体啥意思不知道)
照例我们加上列:
- Total:总共占用内存
- Flat:函数分配的内存,不包含它调用其他函数造成的内存分配。
- Flat%:Flat / Total
- Sum%:自己和前面所有的 Flat% 累积值
- Cum:这个函数分配的内存,以及它调用其他函数分配的内存之和。可以解读为因为这个函数所造成的所有内存分配。
- Cum%:Cum / Total
解读源码
和 CPU 源码解读差不多:
(pprof) list < 函数>例:FindLoops
Total: 82.4 MB
ROUTINE ====================== main.FindLoops in /home/rsc/g/benchgraffiti/havlak/havlak3.go
56.3 56.3 Total MB (flat / cumulative)
...
1.9 1.9 268: nonBackPreds := make([]map[int]bool, size)
5.8 5.8 269: backPreds := make([][]int, size)
. . 270:
1.9 1.9 271: number := make([]int, size)
1.9 1.9 272: header := make([]int, size, size)
1.9 1.9 273: types := make([]int, size, size)
1.9 1.9 274: last := make([]int, size, size)
1.9 1.9 275: nodes := make([]*UnionFindNode, size, size)
. . 276:
. . 277: for i := 0; i < size; i++ {9.5 9.5 278: nodes[i] = new(UnionFindNode)
. . 279: }
...
. . 286: for i, bb := range cfgraph.Blocks {. . 287: number[bb.Name] = unvisited
29.5 29.5 288: nonBackPreds[i] = make(map[int]bool)
. . 289: }
...
可以发现 L288 占用了 29.5M 内存。用 -inuse_objects 来观察,可以看到分配次数:
$ go tool pprof --inuse_objects havlak3 havlak3.mprof
Adjusting heap profiles for 1-in-524288 sampling rate
Welcome to pprof! For help, type 'help'.
(pprof) list FindLoops
Total: 1763108 objects
ROUTINE ====================== main.FindLoops in /home/rsc/g/benchgraffiti/havlak/havlak3.go
720903 720903 Total objects (flat / cumulative)
...
. . 277: for i := 0; i < size; i++ {311296 311296 278: nodes[i] = new(UnionFindNode)
. . 279: }
. . 280:
. . 281: // Step a:
. . 282: // - initialize all nodes as unvisited.
. . 283: // - depth-first traversal and numbering.
. . 284: // - unreached BB's are marked as dead.
. . 285: //
. . 286: for i, bb := range cfgraph.Blocks {. . 287: number[bb.Name] = unvisited
409600 409600 288: nonBackPreds[i] = make(map[int]bool)
. . 289: }
...